Depending on which part of the UK you are testing there are different quality assured testing schemes. According to the College Of Optometrists, if you are not officially certified with your local Diabetic Eye Screening scheme, you can not use the term ‘Diabetic Screening’ when assessing your patients. If a patient is not part of their local NHS Diabetic Eye Screening Programme, you should offer them a dilated fundus exam along with retinal photography.
A detailed Diabetic Eye Screening should include:
Detailed History and Symptoms
- Date of diabetes diagnosis and whether they have type 1 or 2
- Is the diabetes well controlled or not
- Is it diet controlled or are they taking medications, insulin or both
- What other medications are they taking and for what
- Do they have high blood pressure, high cholesterol or any other health concerns
- Do they have any other complications related to diabetes for example any problems with their kidneys or feet
- Do they smoke
- Are they overweight
Vision check (Aided or pinhole VA)
- Check their aided visual acuity (VA) if possible
- If their VA is below 6/9 check it with a pinhole to see if it improves
Intraocular Pressure Check
- Preferably check with contact tonometry
- If IOP over 21, check pachymetry and adjust IOP accordingly
- If IOP over 28, do not dilate and discuss with an Ophthalmologist if working in a hospital setting
Dilate
- Check anterior chamber angle prior to instilling the drops (using van hericks or gonioscopy)
- Instruct patient to wait for 20-30 minutes prior to examination
- Once dilated, you can choose to screen by taking a photo or by using a slit lamp
- Normal procedure is to take a photograph if the media is clear enough and the pupil is dilated efficiently
- If the patient is a poor dilator or has significant cataracts, a slit lamp examination is required
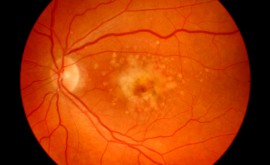
What you are looking for and how to grade
Grading system:
R0M0 – no diabetic retinopathy
R1MO -background peripheral retinopathy but no maculopathy
R1M1 – background retinopathy with macular retinopathy (note – even if the macular is only involved and there is no peripheral retinopathy, it is still R1M1, R0M1 DOES NOT EXIST)
R2M0 – pre – proliferative peripheral retinopathy but no maculopathy
R2M1 – pre-proliferative peripheral retinopathy and maculopathy
R3MO – proliferative peripheral retinopathy and no maculopathy
R3M1 – proliferative peripheral retinopathy and maculopathy
| Grade | Other Terms | Symptoms | Fundus exam | Action |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RO | No DR/grade O | No | Normal retina | review 12/12 or 18/12 |
| R1 | Mild non or pre -proliferative/background DR/grade 1 | No/VA loss if M1 | Microaneurysms (MAs) and haemorrhages, few Cotton Wool Spots (CWS) | review 12/12 if in hosp setting, otherwise refer |
| R2 | non/pre- proliferative DR (can be moderate or severe) Grade 2/3 | No/VA loss if M1 | Extensive MAs, haemorrhages, CWS, pre-retinal haemorrhage, mild IRMA | refer to Ophthalmologist at HES |
| R3 | Proliferative DR/grade 4 | VA loss, flashes and floaters | All of above plus new vessels at the disc or else where (NVD/NVE). Vitreous heamorrhage and retinal detachment possible here | Urgent referral to Ophthalmologist at HES |
| R3s (s=stable) | Treated proliferative retinopathy | No new leakage or new vessels | Review 12/12 | |
| M0 | No maculopathy | Review 12/12 | ||
| M1 | Diabetic Maculopathy | Maculopathy varies: Mild maculopathy:
Clinically Significant Macular Oedema (CSMO) CSMO is when there is leakage within the foveal area and VA is below 6/12. Exudative maculopathy: Leakage, retinal thickening, MAs, hard exudates at the macula. Ischaemic form can have a featureless macular with NVE and poor vision. | Refer to HES | |
| P | Photocoagulation/Grade 4b | Glare, reduced night vision | Small peripheral retinal scars where laser has been done | |
| UG/OL | Un-gradable/Other lesion | Possible reasons for Ungradable include cataracts/corneal haze/poor dilator. If other lesion is seen, refer for assessment | ||